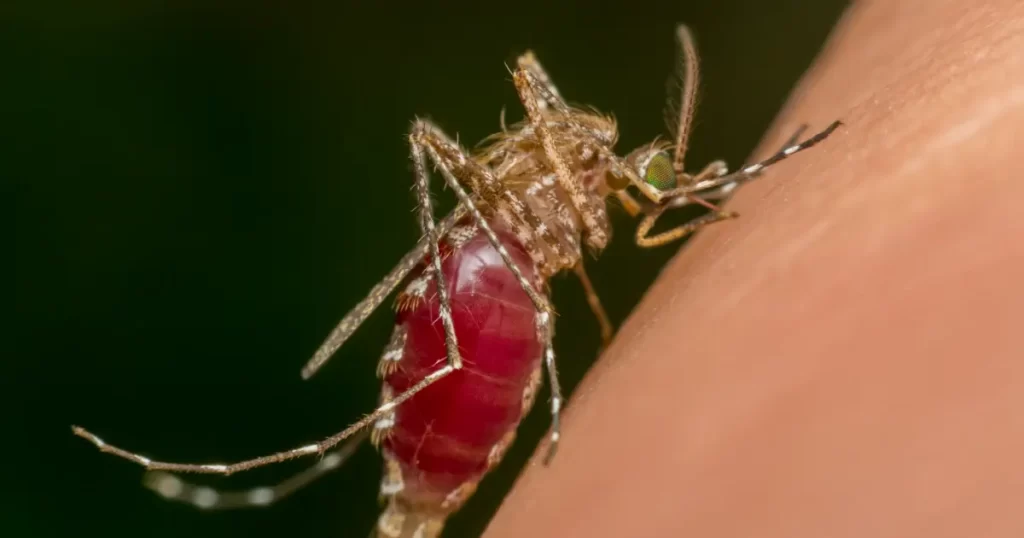
- Two African countries—Angola and Nigeria—have reported new circulating vaccine-derived poliovirus type 2 cases (cVDPV2) cases this week, according to the latest weekly update from the Global Polio Eradication Initiative (GPEI). Angola’s patient had a paralysis onset of January 6, marking the country’s first case of the new year. Nigeria reported three cases, all with onsets in January and February, bringing its total for 2025 to 10. In other developments, wastewater surveillance in Israel detected a positive cVDPV2 sample collected on January 29 from Central province, a densely populated area. Genetic analysis suggests the virus isn’t related to recent environmental detections in Europe or Gaza and is most closely related to a strain that originated in Nigeria’s Zamfara state.
- In its monthly mpox situation update covering activity through February, the World Health Organization (WHO) noted several new developments regarding the spread of different mpox clades, including the first imported cases involving the novel 1b clade in Brazil and the United Arab Emirates (UAE), raising the number of countries outside Africa reporting the clade to 15. The WHO also said at least seven other countries have reported imported clade 1b cases linked to UAE travel, suggesting likely community transmission. Inside Africa, the Republic of Congo and Tanzania also reported their first clade 1b mpox detections. In other developments, the WHO said increasing outbreaks of clade 2b mpox is a concerning new development. Until recently, clade 2b had only rarely been detected in people and was mainly seen in animal populations. However, since 2024, the clade 2b has been detected in adults and children in Ivory Coast, Ghana, Guinea, and Liberia, many with unknown epidemiological links. The WHO also said health officials are tracking a clade 1a lineage spreading through sexual contact in the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC) capital Kinshasa, where sustained transmission of clade 1a mpox with high rates of APOBEC3-driven mutations is also occurring.
US flu indicators declined for the sixth week in a row, but levels remain elevated nationally, and activity is expected to continue for the next several weeks, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) said today in its latest weekly update.

Nationally, the percentage of outpatient visits for flulike illness, at 3.3%, remains above the national baseline for the seventeenth consecutive week, but five areas of the country are now below their regional baselines.
Only 7 jurisdictions are still reporting high or very high flu activity, a sharp drop from 20 during the previous week. Test positivity for flu is now at 10.7%, down from 13.3% in last week’s report.
Hospitalizations and deaths are trending downward, but the CDC received reports of eight more pediatric flu deaths, raising the season’s total to 159.
The CDC has defined this season as high severity, and according to its latest estimate, there have been at least 44 million infections, 580,000 hospitalizations, and 25,000 deaths so far.
COVID wastewater levels decline to low
Meanwhile, COVID levels also continue to decline from already low levels, according to the CDC’s latest data updates. Wastewater detections last week declined from the medium to the low level, with detections highest in the South. The proportion of overall deaths that were from COVID last week was 0.9%, lower than the 1.5% for flu.
In its latest variant estimates, the CDC said the proportion of LP.8.1 viruses continues to rise, making up 55% last week, well above the declining levels of XEC, which is at 21%. LP.8.1 is a descendant of KP.1.1.3, which is part of the JN.1 lineage.
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) today approved the first at-home, over-the-counter test for chlamydia, gonorrhea, and trichomoniasis.
The Visby Medical Women’s Sexual Health Test is a single-use test intended for women with or without symptoms. The FDA granted marketing authorization to Visby Medical based on testing that showed the device correctly identified 98.8% of negative and 97.2% of positive Chlamydia trachomatis samples, 99.1% of negative and 100% of positive Neisseria gonorrhoeae samples, and 98.5% of negative and 97.8% of positive Trichomonas vaginalis samples.
The test, which includes a sample collection kit and a powered testing device that communicates testing results to an app, can be bought without a prescription and deliver results within 30 minutes.
Expanding access to tests could boost diagnosis, treatment
Courtney Lias, PhD, director of the Office of In Vitro Diagnostic Devices in the FDA’s Center for Devices and Radiological Health, said the ability to test at home is particularly important for patients who are concerned they may have a sexually transmitted infection and may experience fear or anxiety about getting tested, which could result in a delayed diagnosis.
“Expanding access to tests for sexually transmitted infections is an important step toward earlier and increased diagnosis, which can result in increased treatment and reduced spread of infection,” Lias said in an FDA press release.
According to the most recent data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, more than 2.2 million US cases of gonorrhea and chlamydia were reported in 2023, while trichomoniasis affects roughly 2.6 million Americans.
The FDA says it reviewed and approved the device under a new regulatory pathway that allows makers of medical devices to obtain marketing authorization by demonstrating substantial equivalence to an approved device.